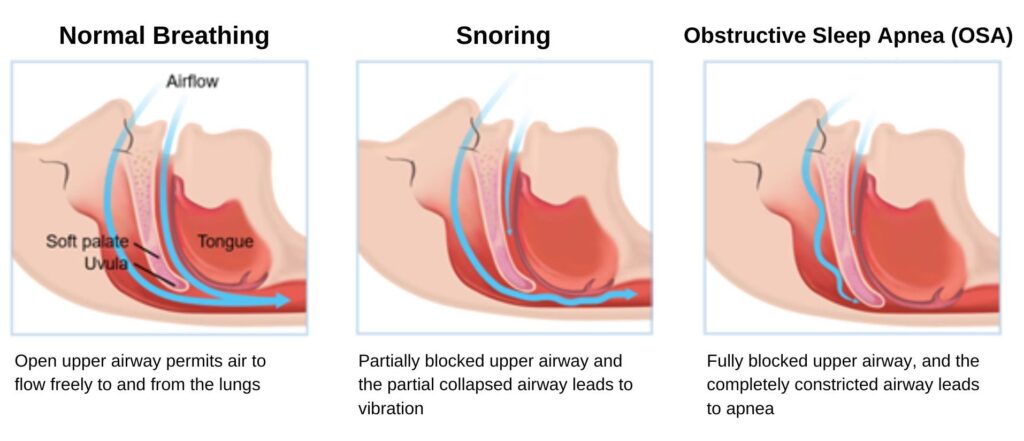
Snoring and sleep apnea are common sleep disorders that can significantly impact an individual’s health and quality of life. Snoring is characterized by the vibration of respiratory structures during sleep due to obstructed air movement. On the other hand, sleep apnea is a more severe condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep.
Sleep apnea (Sleep apnoea) is a condition where individuals frequently stop breathing in sleep, leading to disruptions that affect overall health and energy levels. When someone repeatedly stops breathing in sleep, their oxygen levels drop, triggering the brain to wake them slightly, often without them even realising it. People who stop breathing in sleep may experience symptoms like loud snoring, daytime fatigue, and difficulty concentrating, which are common signs of sleep apnea.
Why do we snore?
Snoring is a noisy breathing phenomenon that occurs during sleep, typically due to the relaxation of muscles in the throat and airway. This relaxation causes the tissues to vibrate as air passes through, resulting in the characteristic sound of snoring. While snoring is often considered a nuisance, it can also be a symptom of underlying health issues, such as obstructive sleep apnea.
Several factors contribute to a person snoring:
- Obstructed Airway: Blockages or narrowing of the airway, often due to relaxed throat muscle, anatomical abnormalities, and sleep apnea, can lead to snoring.
- Muscle Relaxation: During sleep, the muscles in the throat and tongue relax, narrowing the airway and increasing the likelihood of snoring.
- Nasal Congestion: Conditions such as allergies or sinus infections can cause nasal congestion, further obstructing airflow and contributing to snoring.
While snoring may seem harmless, it can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to daytime fatigue and other health issues. Excess weight can contribute to snoring, but people of all body types can experience snoring due to various factors such as anatomy and muscle tone. Through proper lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, it is possible to reduce or eliminate snoring and improve sleep and also overall health
Also Read: Insomnia – Treatment & Management
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a very serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated pauses in breathing or shallow breaths during sleep. These pauses, known as apneas, can last from a few seconds to minutes and may occur multiple times throughout the night. Sleep apnea is classified into 3 main types:-
- Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
- Central sleep apnea (CSA), and
- Mixed sleep apnea.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is the most common form of sleep apnea, occurring when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, leading to a partial or complete blockage of the airway. This obstruction results in interrupted breathing and disrupted sleep patterns. Excess weight, particularly around the neck, can contribute to airway obstruction and increase the likelihood of sleep apnea. Sleep apnea becomes more common as individuals age, with middle-aged and older adults at higher risk. A family history of sleep apnea or other sleep disorders also can predispose individuals to developing the condition.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) occurs when the brain fails to send the appropriate signals to the muscles responsible for breathing during sleep. Unlike OSA, there is no physical obstruction of the airway in CSA. Instead, breathing pauses are caused by a lack of respiratory effort. Mixed Sleep Apnea is also known as complex sleep apnea, is a combination of both obstructive and central sleep apnea, where individuals experience characteristics of both types.
Snoring is a hallmark symptom of sleep apnea, especially in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Interrupted breathing / temporary stopping of breathing is a key indicator of sleep apnea. Due to disrupted sleep patterns, individuals with sleep apnea often experience daytime fatigue, drowsiness, and difficulty concentrating.
Signs of Sleep Apnea
- Common warning signs of sleep apnea include loud snoring, waking up gasping for air, and feeling excessively tired during the day.
- If you or a loved one experience frequent headaches in the morning, irritability, or memory problems, these also may be warning signs of sleep apnea.
- Recognizing such warning signs of sleep apnea early—like pauses in breathing, restless sleep, and dry mouth in the morning—can lead to timely and effective treatment.
- Some of the most overlooked warning signs of sleep apnea include difficulty staying asleep, nighttime sweating, and frequent trips to the bathroom at night.
Untreated, the warning signs of sleep apnea can lead to serious health issues, so it’s important to address symptoms with a healthcare provider.
Impact of Snoring & Sleep Apnea
Snoring and apneas reduce the amount of oxygen in the blood, potentially damaging the brain and even causing heart attacks. Many wonder, Is it okay to live with sleep apnea? However, sleep apnea is always associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, coronary artery disease, and stroke. The repeated cycles of oxygen deprivation and arousal from sleep strain the cardiovascular system, leading to adverse health outcomes.
Sleep apnea also impairs cognitive function, affecting memory, concentration, and decision-making abilities. Individuals with untreated sleep-disordered breathing, including snoring and apneas, may experience difficulties with learning, problem-solving, and overall cognitive performance. Daytime sleepiness and fatigue resulting from poor sleep quality due to snoring and sleep apnea can also increase the risk of accidents, both on the road and in the workplace. Individuals with untreated sleep apnea are more likely to experience motor vehicle accidents and workplace injuries.
The combination of physical symptoms, cognitive impairment, and emotional distress associated with sleep apnea can significantly impact an individual’s overall quality of life and psychological well-being. This condition has been linked to an increased risk of depression and anxiety disorders. The chronic stress of sleep disruption and the impact on daily functioning can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mood disorders. Sleep deprivation also impairs emotional regulation and increases irritability, mood swings, and emotional reactivity.
Snoring and sleep apnea can also impact relationships and social interactions. Loud snoring and frequent awakenings may disrupt the sleep of bed partners, leading to frustration and strain in relationships. Excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue may limit participation in social activities and impair interpersonal relationships, leading to feelings of isolation and depression. While there may not be a single way to completely fix sleep apnea, managing sleep-disordered breathing through lifestyle changes and treatment options can vastly improve quality of life and overall well-being.
Diagnosing & Treating Sleep Apnea
Sleep Study
There is not a single sleep apnea cure; however, a combination of lifestyle changes and treatments can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life. Sleep Study (Polysomnography) is the gold standard diagnostic test for sleep apnea. It involves monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep, including brain activity, eye movements, muscle activity, heart rate, and breathing patterns. At SOLVEMyHealth, we recommend such a comprehensive assessment to evaluate the severity of apnea and determine appropriate sleep apnea (apnoea) treatment options. We also provide home sleep apnea tests, which includes portable devices that individuals can use to monitor their sleep patterns in the comfort of their own home. While not as comprehensive as polysomnography, these tests also can provide valuable information to screen for sleep apnea and guide further evaluation for obstructive sleep apnea treatment.
Medical Interventions for Sleep Apnea (Apnoea)
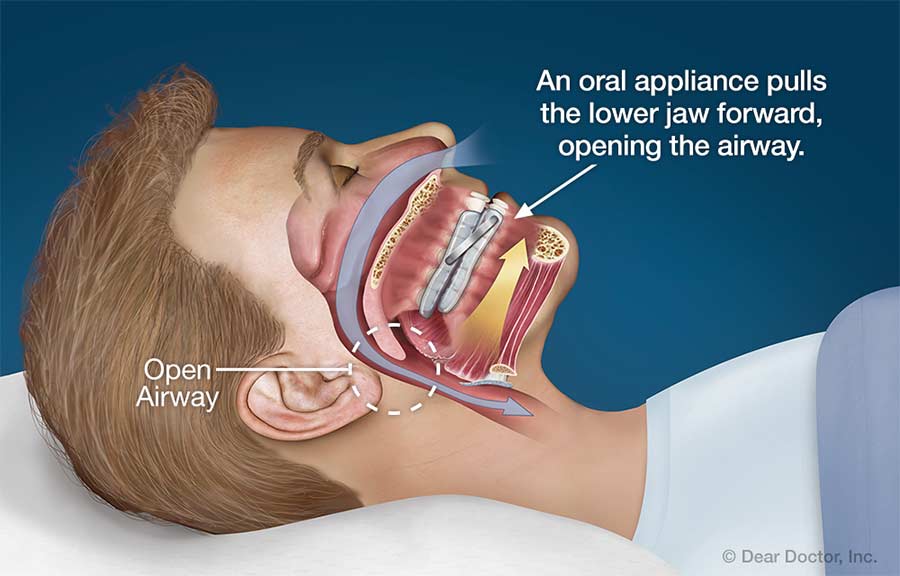
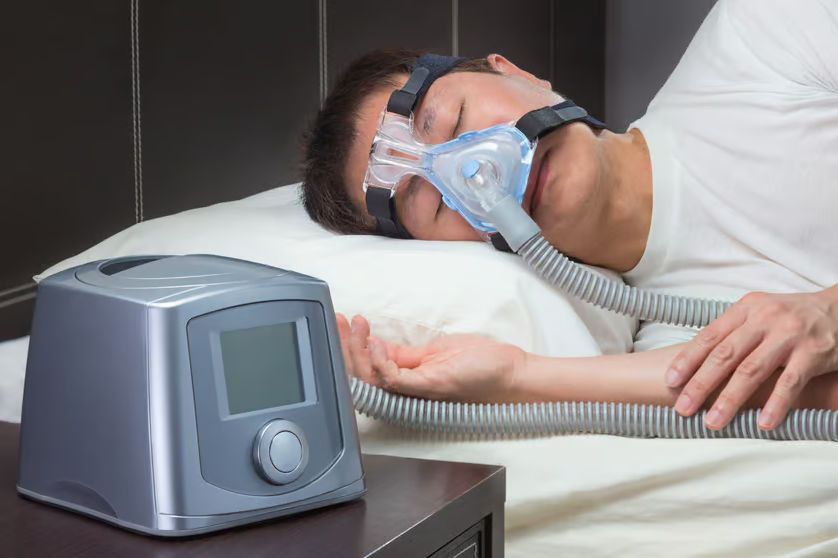
Is sleep apnea treatable? Very much, yes! Based on the severity of the apnea and potential risks, medical management is required. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is the most common and effective obstructive sleep apnea (apnoea) treatment. It involves wearing a mask connected to a machine that delivers a continuous stream of air pressure to keep the airway open during sleep, preventing episodes of apnea and snoring.
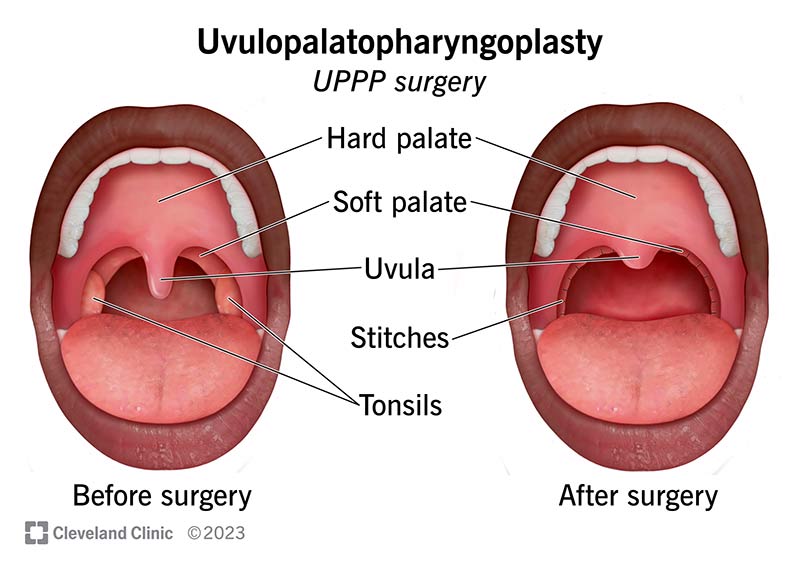
Oral appliances, such as mandibular advancement devices, also can help reduce snoring and mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea by repositioning the lower jaw and tongue to keep the airway open. These devices are custom-fitted by a dentist and worn during sleep. In certain cases, surgical interventions may be considered for those with severe obstructive sleep apnea who have not responded to other sleep apnea treatment options. Surgical procedures, such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) or maxillomandibular advancement are done, to remove or reposition obstructive tissues in the throat or lower jaw and thus improve airflow during sleep.
Lifestyle Interventions for Sleep Apnea
Many people search for a sleep apnea cure, but success often comes from a personalized approach that includes weight management, therapy, and consistent sleep habits. Losing excess weight, particularly around the neck and throat area, can help reduce severe snoring and improve symptoms of sleep apnea. At SOLVEMyHealth, we help our clients by handholding and advising them through a combination of healthy eating habits, regular exercise, and behavioral modifications that support sustainable weight loss efforts to manage sleep apnea and address both sleep and stress. Sleeping on the back can exacerbate snoring problems and sleep apnea by allowing the tongue and soft tissues in the throat to collapse more easily. Sleeping on the side or using positional therapy devices can help prevent airway obstruction and reduce symptoms, helping individuals get sleep more easily. Alcohol and sedative medications relax the muscles in the throat and tongue, increasing the likelihood of airway collapse and worsening snoring and sleep apnea. Limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption and sedative use before bedtime is important to improve sleep quality and reduce symptoms.
How can we help you?
If you or someone you know seems to stop breathing in sleep, it may be time to consult a specialist to assess for sleep apnea and explore effective treatments. Lifestyle changes, such as weight management and regular exercise, can be effective ways to stop sleep apnea or reduce its severity. At SOLVEMyHealth, we offer comprehensive support to manage snoring and sleep apnea effectively. Our team of dedicated doctors specializes in identifying root cause and severity of your condition, ensuring personalized care. We understand the importance of convenience, which is why we provide the option of conducting sleep studies in the comfort of your own home. If required, we offer CPAP machines for rental or purchase to assist in sleep apnea treatment. Our experienced team carefully assesses the results of diagnostic tests and collaborates with you to develop a tailored sleep apnea treatment plan. For those looking to stop sleep apnea, early diagnosis and a tailored treatment plan are key to managing symptoms effectively.
Additionally, we recognise the significance of addressing underlying health issues, such as obesity, diabetes, heart diseases, and hypertension, which can exacerbate sleep apnea. Our expert team provides diet plans, exercise plans and comprehensive support to help you lose weight and make necessary lifestyle changes, offering continuous follow-ups and guidance to ensure success in managing your condition. If you are hoping for a sleep apnea cure, consult us to explore the best treatment options tailored to your needs. From improving sleep hygiene to using advanced devices, there are several strategies to help stop sleep apnea and enjoy a restful night











1 comment
This was so easy to read! Thanks for the tips.